
Tackling AI Bias: Identifying & Preventing Discrimination
13 Min read
Artificial intelligence (AI) has the potential to revolutionize numerous industries, but it is not without its pitfalls. …

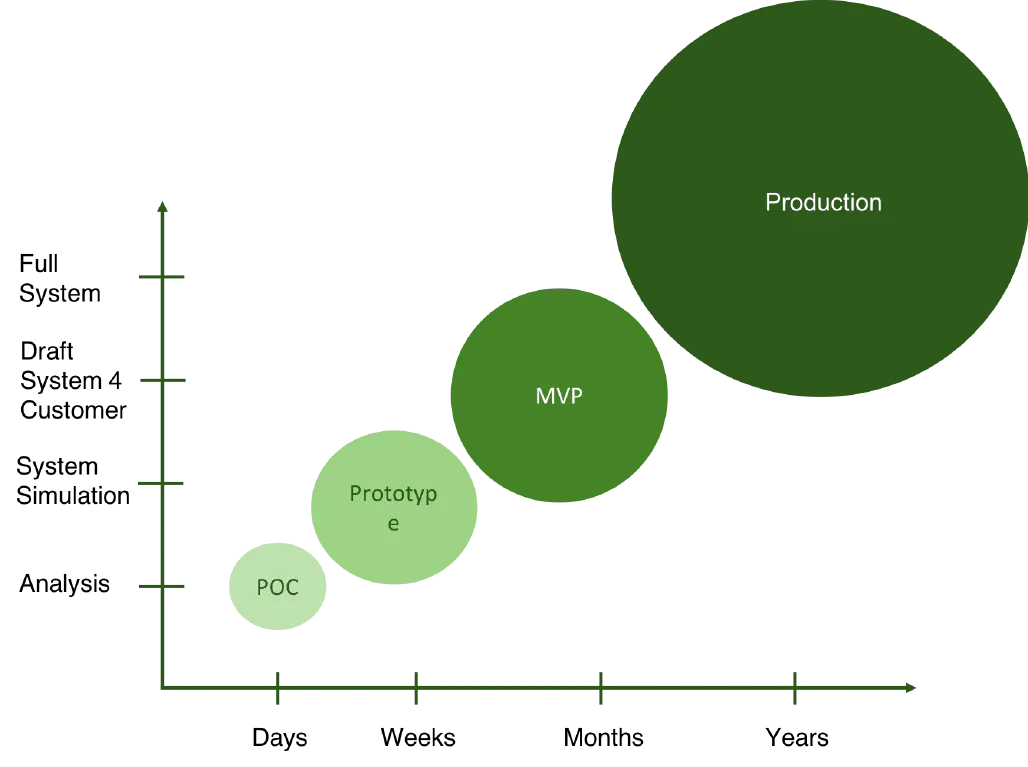
If you are interested in understanding what's the difference between these terms, you are in the right place. When it comes to developing a new product or adding a new feature, you must first test it. Checking your idea using the necessary processes is the greatest approach to do it. There are various stages of the software product: proof-of-concept, prototype, MVP, and so on.
What is the difference between a proof of concept and a minimum viable product (MVP)? Why are these stages so important? When is it appropriate to create a Minimum Viable Product?
This post focuses on two basic ways that can help you quickly test your idea and develop an effective solution.
Proof of concept, or PoC, is a small project designed to verify that a particular idea is feasible. Usually, companies develop it for internal testing. Various fields use proof of concept to test their innovations.
For example, Jeff Bezos, a co-founder of Amazon, came up with an online store idea when he couldn't buy a new book. Instead of spending seed funds for inventory, he tried selling books first to see how his idea would work.
Jeff proved that people would buy shoes books and expanded for other categories. Also, he discovered which items were in trend. With this proof of concept, Jeff was confident enough to purchase inventory and scale his business.
The whole aim of a PoC is to show whether it is possible to develop the functionality in the real world. It also indicates the potential obstacles for the product being developed and accepted by users. The final PoC design should not be flawless, but it presents the concept's viability before you jump into development.
The following questions are answered through proof of concept:
Using a proof of concept to test your idea allows you to grasp its usefulness for actual people at an early stage. PoC provides you an idea of what technology, funding, and time you'll need to develop a feature or a product, whether it's for a feature or a product. This aids you in developing a business strategy for the feature you've chosen.
Although these names appear to be interchangeable, they refer to separate stages of growth. The first phase is a proof of concept, followed by a prototype. The proof-of-concept (PoC) establishes the product's practicality, after which a prototype is produced.
A proof of concept (PoC) is a general proof and a concise outline of a concept. A comparison between the idea draft and its visual implementation is actually proof of concept vs. prototype. The prototype is a rough model that brings the PoC idea to life and incorporates key design components. It determines the user experience (UX) of the proposed software, including its structure, functionality, and user flow. Prototype photos for a custom healthcare app developed by CloudFlex, for example, can be found below.
A minimum viable product, or MVP, is an early version of a product that contains all of the essential functionality. This version provides enough value for clients to provide early feedback before you invest a lot of time on something they don't want or need.
Why is MVP employed in the creation of software products?
A minimal viable product (MVP) is a version that can be used by potential customers. It's not a feature-bare product, but rather an early, usable version of your solution that iterates functionality in the future.
It is possible to put a minimal viable product on the market. As a result, it is a model that can be sold to customers rather than a prototype that is solely used by the product team.
An MVP allows you to see how your product will be received by your target audience. Users can test it out, and if they enjoy it, they'll tell their friends about it. Then you may determine whether you want to add more features to your minimum viable product or focus on improving it.
For example, a corporation may release an MVP version for a certain region before introducing a global product. If the company receives great feedback from users, it may expand to other countries.
A modular structure is present in a minimum viable product. As a result, your product's development team will be able to easily remove unneeded elements and other flaws. This improves the user's experience.
The minimal viable product reduces the time and expense of providing a solution since it only comprises the essential elements.
Dropbox is an excellent example of conserving resources in preparation for a product launch. Drew Houston set out to see if people were interested in file-sharing software. As a result, he produced a three-minute video describing the service work process and aimed it at early adopters. Overnight, the video attracted 75000 people who were eager to get their hands on the solution. Dropbox is now valued at roughly $9 billion.
The proof of concept and the minimal viable product are distinct in that they serve different functions. PoC provides theoretical support for a solution or a specific function. Meanwhile, MVP implements the elements that were developed during the proof-of-concept and prototype stages.
The difference between a proof of concept and a proof of concept is analogous to the difference between an idea draft and an idea realization. A proof of concept details the technologies that will be used to implement a solution and investigates the idea's potential dangers and technical challenges. Its purpose is to assess the product's prospective market demand. On the other hand, MVPs are built with the primary objective of determining how customers react to a product.
Although skipping this stage may appear to save time, proof of concept is critical for product development. It emphasizes the most important components of your business concept. Is it feasible to put the desired features in place? What are the potential stumbling blocks? How much money would you make?
Before putting your concept into action, you must first answer these questions.
Startup founders frequently feel that their concept will alter the world for the better and solve the problem of their target audience. Proof of concept allows you to see if your ideas is viable. If your notion looks to be unworkable, it will be easier to come up with a different solution during the proof-of-concept stage.
The whitepaper on Bitcoin, which was released in 2008, shows how to back an idea from the start. It's a proof-of-concept document in which Satoshi Nakamoto describes a problem and proposes a solution.
The paper also defines blockchain and discusses how Bitcoin helps society. This Proof of Concept has created a field that allows for additional payment and trade methods.
PoC allows you to set your solution apart from those offered by competitors. Consider the case when products identical to what you intend to produce, such as a messaging app, are already successful. As a result, it's best to have a proof of concept that demonstrates unique functionality and distinguishes your product from competing options.
You must first convince potential investors that your project is worthwhile before requesting money. A summary of the project's underlying meaning and an explanation of why the suggested idea is practical and profitable may be included in the proof of concept. All of these could help you persuade investors to fund your idea.
PoC identifies possible risks and challenges when you find a feature or a solution. This is critical for large-scale initiatives involving significant financial outlays. Proof of concept ensures that you don't go over budget or time, and that all of your features are functional.
PoC is a good decision for early startups to test if the assumptions are correct
In your proof-of-concept, you demonstrated the concept of your product and sketched out the early design. You may now create an MVP to test the functionality of your solution.
The minimal viable product allows you to deploy your product with only the most essential features as soon as feasible. Although your solution lacks various capabilities, it is adequate to sell the product on the market. As a result, you form early ties with your future customers. If people appreciate your MVP, you know it's worth continuing to work on it.
Because a minimum viable product only includes the most essential functionality, your team will spend less time developing your project. This reduces the time and money spent on solution development.
MVPs recommend the essential value to users. Launching a minimal viable product allows you to see if your solution meets the demands of specific people. The feedback from the audience allows you to double-check your assumptions. Then you must choose between iterating features and perfecting your product.
To join the market, a minimum viable product requires the least amount of work and key functionality. You don't have to create a full-fledged solution for your potential consumers, but it should include the necessary components. Users may more easily provide feedback on the products they use and gain experience with. You may improve your product by understanding market perspective.
Act carefully and build PoC first and MVP after if you have budgeting limitations
It's similar, but it isn't the same. They are used in software development for certain purposes. The phases for such early introduction of a product are known as proof of concept (POC) and minimum viable product (MVP). When you apply your solution, they save you time, money, and effort. If you have an idea and want to check if it works in the actual world, you'll need proof of concept. Following that, you'll have to have a prototype and a minimal viable product to obtain feedback among early adopters. Regardless of the fact that they are all part of the same process, they arrive to distinct results. Let's look at how they relate in the table below.
| PoC | Prototype | MVP | |
|---|---|---|---|
| What is it? | Theoretical validation of an idea's feasibility | Visual representation of a tried-and-true concept | A simple form of a product that may be used |
| What do you create it for? | To determine the project's viability. | Basic features, structure, and user workflow | Users will be using an early version of the product |
| How long does it take to develop it? | 2 days - 1 week | 1 - 4 weeks | 4 - 6 months |
| What features should it use? | Describe the technology that will be employed | UI design is not included in UX design. | UX/UI are among the most important elements |
| When should you choose it? | When you need to determine scalability, risk, length, budget, and income | When you require a rough draft for further work | When you need to launch quickly and gather client feedback |
| How do you test it? | Only the development team and stakeholders are allowed to work on the project internally | Internally and with a small number of people | Users who are your target audience |
| When do you show it to investors? | Pre- / Seed funding | Seed / A round | A / B round |
After you've come up with an idea, you'll want to put it to the test. Proof of concept and minimal viable product are powerful approaches in this situation. Both provide you the opportunity to test your hypothesis and receive early feedback. The difference between a PoC and an MVP, on the other hand, is the same as the difference between a draft and a completed project.
You use a proof-of-concept to see if your idea is viable. Building a minimal viable product, on the other hand, entails establishing a market-ready solution that will generate feedback from early adopters.
Both stages are necessary for creating a product that meets people's demands while also being scalable in the future.

13 Min read
Artificial intelligence (AI) has the potential to revolutionize numerous industries, but it is not without its pitfalls. …

12 Min read
Quantum computing and artificial intelligence (AI) are two of the most revolutionary technological domains that are …
Looking for a solid engineering expertise who can make your product live? We are ready to help you!
Get in Touch